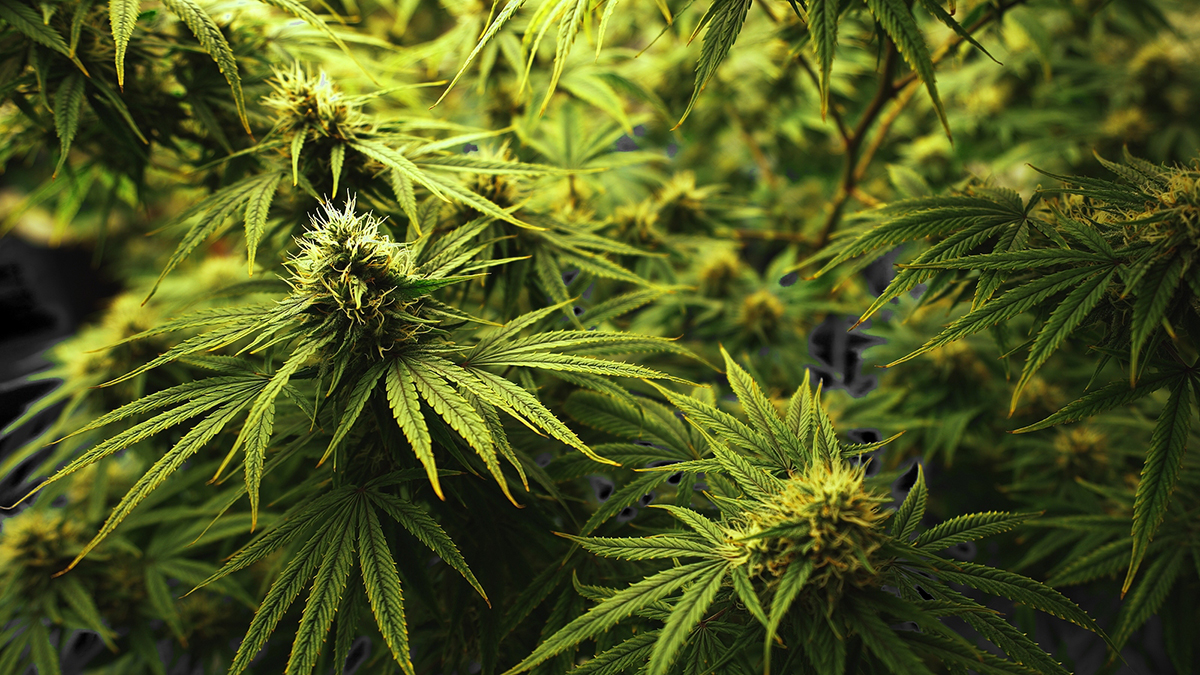
 This herb has been proven to improve and even cure several serious diseases.
This herb has been proven to improve and even cure several serious diseases.
Next in line: dementia!
Three recent studies have found that this herb can halt and even reverse Alzheimer’s and other forms of dementia.
There is only one problem: It is illegal in most places.
All three studies had approximately the same structure.
Throughout your body, there are things called type 2 cannabinoid receptors. Diseases can develop when these receptors are too inactive. If we want to treat these diseases, we must do something to stimulate and energize these receptors.
Fortunately, there is a natural substance that does just this. It’s called cannabis. The cannabis plant’s ability to stimulate these receptors is the foundation for most arguments for medical marijuana.
Three new studies all demonstrate that activation of type 2 cannabinoid receptors can treat Alzheimer’s disease and dementia.
Study 1: Alzheimer’s Reversed
In the first study, published in Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, Indian researchers tested the ability of 1-phenylisatin, a type 2 cannabinoid receptor agonist, to ameliorate the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease.
They first induced Alzheimer’s disease in rats and verified that the rodents’ memories were indeed compromised by observing their efforts to learn a route through a maze.
The researchers then gave the rodents 1-phenylisatin, which activated their type 2 cannabinoid receptors. Subsequent tests revealed that the rats’ memories and executive function improved, the oxidative stress in their brains reversed, and the progressive physical damage to their brains halted and even reversed.
Study 2: Vascular Dementia Reversed
In the second study, published in the journal Current Neurovascular Research, scientists targeted vascular dementia, the second most common form of dementia behind Alzheimer’s disease.
They tried to attack the chronic cerebral hypoperfusion that gives rise to vascular dementia. Vascular dementia occurs when there is an insufficient blood supply to the brain, and chronic cerebral hypoperfusion is a condition wherein the blood supply to the brain is inadequate.
Using a methodology similar to that of the first study, the researchers induced chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in rats to cut off the blood supply to their brains. This soon resulted in vascular dementia, which they verified through maze memory tests and executive function tests, which the rats predictably failed.
The researchers then injected the rats with 1-phenylisatin to stimulate their cannabinoid receptors. As with the Alzheimer’s disease sufferers in the first study, the rats’ memories and executive function improved, and there was also a significant reduction in the physical and chemical brain damage brought about by the disease.
Study 3: Advanced Alzheimer’s Reversed
Researchers in the third study, published in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, administered THC and CBD, the two main components of cannabis, to mice with dementia. They expected that this would reverse memory loss for mice with early dementia but possibly not for mice with advanced dementia.
They were pleasantly surprised to find that the treatment improved the memory of both groups of mice, although it could not reverse as much of the physical brain damage for those with advanced dementia as it could for those with early-stage dementia.
There are just two problems:
1) Cannabis is illegal in most regions of the world.
2) You may not want to get high on cannabis.

 Overcoming IBD
Overcoming IBD Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple Sclerosis Banishing Bronchitis
Banishing Bronchitis Gum Disease Gone
Gum Disease Gone Overcoming Onychomycosis
Overcoming Onychomycosis Neuropathy No More
Neuropathy No More The Prostate Protocol
The Prostate Protocol Brain Booster
Brain Booster
 Ironbound
Ironbound
 Solution for Shingles
Solution for Shingles
 The Bone Density Solution
The Bone Density Solution
 The Ultimate Healing Protocol
The Ultimate Healing Protocol
 The Parkinson's Protocol
The Parkinson's Protocol
 The Chronic Kidney Disease Solution
The Chronic Kidney Disease Solution
 Overthrowing Anxiety
Overthrowing Anxiety The Fatty Liver Solution
The Fatty Liver Solution The Hypothyroidism Solution
The Hypothyroidism Solution
 The End of Gout
The End of Gout The Blood Pressure Program
The Blood Pressure Program
 The Oxigized Cholesterol Strategy
The Oxigized Cholesterol Strategy
 Stop Snoring And Sleep Apnea Program
Stop Snoring And Sleep Apnea Program
 The Arthritis Strategy
The Arthritis Strategy The Vertigo & Dizziness Program
The Vertigo & Dizziness Program The 3-Step Diabetes Strategy
The 3-Step Diabetes Strategy Hemorrhoids Healing Protocol
Hemorrhoids Healing Protocol The Erectile Dysfunction Master
The Erectile Dysfunction Master Weight Loss Breeze
Weight Loss Breeze The IBS Program
The IBS Program The Insomnia Program
The Insomnia Program The Migraine and Headache Program
The Migraine and Headache Program The Neck Pain Solution
The Neck Pain Solution The Menopause Solution
The Menopause Solution The Ejaculation Master
The Ejaculation Master The TMJ Solution
The TMJ Solution The Acid Reflux Solution
The Acid Reflux Solution The Fibromyalgia Solution
The Fibromyalgia Solution The Psoriasis Strategy
The Psoriasis Strategy