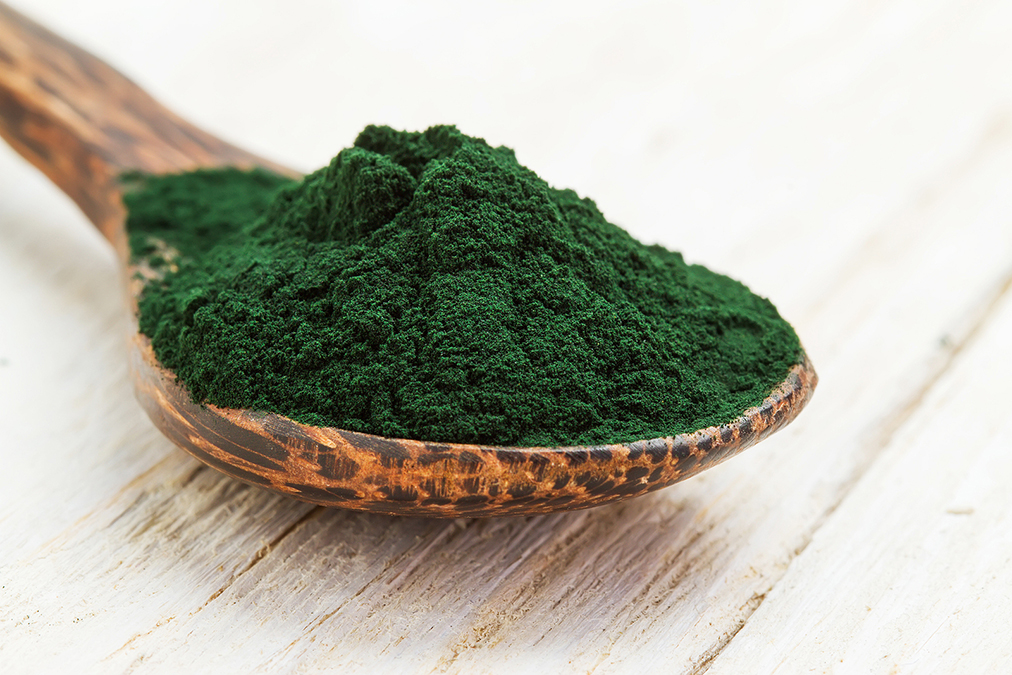
 A common algae drops your blood pressure more than most medications, according to a study in the Journal of Human Nutrition and Dietetics.
A common algae drops your blood pressure more than most medications, according to a study in the Journal of Human Nutrition and Dietetics.
…without any side effects!
Scientists have long wondered why people in coastal areas, especially in Asia, tend to have lower rates of heart disease.
Turns out, many regularly eat seaweed and algae.
These marine plants are full of good stuff: omega-3s, antioxidants, potassium, and unique peptides that protect the heart.
Some even contain natural nitrates, which relax blood vessels and improve circulation.
To investigate further, researchers analyzed 29 clinical trials from 12 countries, covering 1,583 adults aged 18 to 86.
Participants ranged from healthy to those with conditions like obesity, diabetes, or metabolic syndrome.
Only studies lasting four weeks or more were included, since blood pressure shifts take time.
Some trials used microalgae like Spirulina and Chlorella, while others used macroalgae like kelp or wakame.
The algae were given in many forms: powders, drinks, tablets, dried whole algae, or extracts. Doses ranged from 0.001 to 8 grams daily.
Here’s what they found:
-
● Overall: Algae users saw systolic pressure drop by 2.05 mmHg and diastolic by 1.87 mmHg over placebo.
● Spirulina was best: Cutting systolic by 5.28 mmHg and diastolic by 3.56 mmHg.
● Whole algae > extracts: Whole algae reduced systolic by 3.96 mmHg and diastolic by 2.82 mmHg.
● High doses worked best: 3g+ daily lowered systolic by 3.71 mmHg and diastolic by 3.05 mmHg.
● People with health issues (like metabolic syndrome) saw 3x greater improvements than healthy participants.
● Most effective in people with high BP (129/79 mmHg or more).
● Kelp didn’t help, despite containing nitrates.
● Timeframe: Benefits kicked in after 12 weeks.

 Overcoming IBD
Overcoming IBD Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple Sclerosis Banishing Bronchitis
Banishing Bronchitis Gum Disease Gone
Gum Disease Gone Overcoming Onychomycosis
Overcoming Onychomycosis Neuropathy No More
Neuropathy No More The Prostate Protocol
The Prostate Protocol Brain Booster
Brain Booster
 Ironbound
Ironbound
 Solution for Shingles
Solution for Shingles
 The Bone Density Solution
The Bone Density Solution
 The Ultimate Healing Protocol
The Ultimate Healing Protocol
 The Parkinson's Protocol
The Parkinson's Protocol
 The Chronic Kidney Disease Solution
The Chronic Kidney Disease Solution
 Overthrowing Anxiety
Overthrowing Anxiety The Fatty Liver Solution
The Fatty Liver Solution The Hypothyroidism Solution
The Hypothyroidism Solution
 The End of Gout
The End of Gout The Blood Pressure Program
The Blood Pressure Program
 The Oxigized Cholesterol Strategy
The Oxigized Cholesterol Strategy
 Stop Snoring And Sleep Apnea Program
Stop Snoring And Sleep Apnea Program
 The Arthritis Strategy
The Arthritis Strategy The Vertigo & Dizziness Program
The Vertigo & Dizziness Program The 3-Step Diabetes Strategy
The 3-Step Diabetes Strategy Hemorrhoids Healing Protocol
Hemorrhoids Healing Protocol The Erectile Dysfunction Master
The Erectile Dysfunction Master Weight Loss Breeze
Weight Loss Breeze The IBS Program
The IBS Program The Insomnia Program
The Insomnia Program The Migraine and Headache Program
The Migraine and Headache Program The Neck Pain Solution
The Neck Pain Solution The Menopause Solution
The Menopause Solution The Ejaculation Master
The Ejaculation Master The TMJ Solution
The TMJ Solution The Acid Reflux Solution
The Acid Reflux Solution The Fibromyalgia Solution
The Fibromyalgia Solution The Psoriasis Strategy
The Psoriasis Strategy