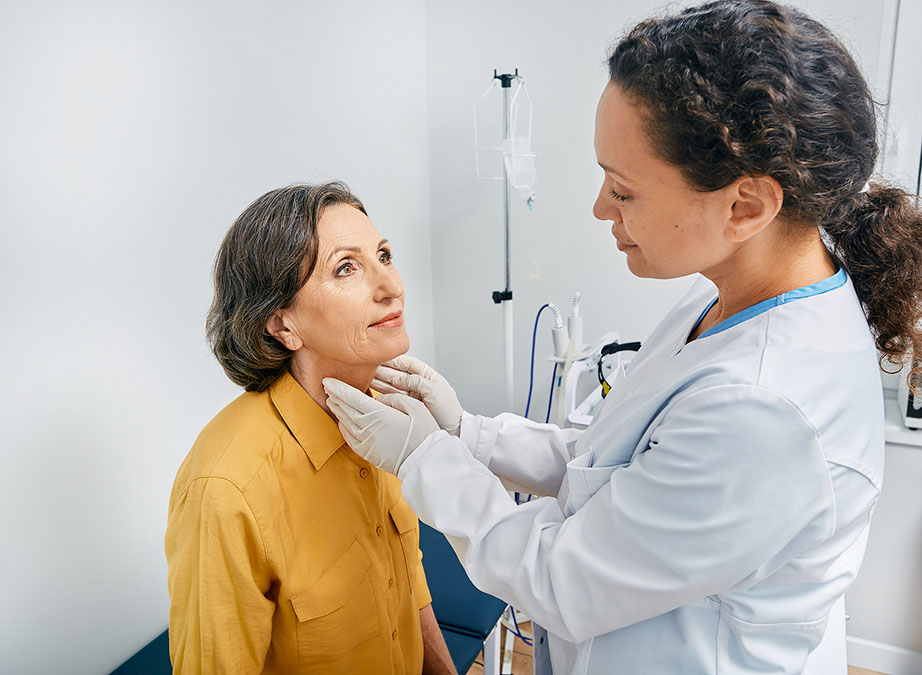
 Hypothyroidism is usually linked to weight gain and reduced energy levels.
Hypothyroidism is usually linked to weight gain and reduced energy levels.
But it can also seriously and painfully affect your mouth.
This is according to a new study published in in the Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.
Oral lichen planus (OLP) is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the mouth and can be quite uncomfortable, with sores on the tongue, inner cheeks, or gums.
It is most common in middle-aged women and can cause lasting issues, because these mouth sores don’t heal easily and can sometimes lead to more serious health concerns like nutritional deficiencies due to the pain of eating, difficulties speaking or chewing, and even oral cancer.
Since the symptoms of hypothyroidism are often vague feelings of depression or fatigue, the authors of this study wondered whether OLP could serve as an easier indication that the thyroid isn’t working properly.
They included 1,200 patients visiting a department of oral medicine and radiology at an Indian hospital in their study. 600 of them had hypothyroidism as identified through their medical records, and 600 not.
After examining all patients for OLP, the results were quite revealing.
-
1. 3.45% of patients with hypothyroidism versus only 1.34% of those without had OLP.
2. Those with hypothyroidism were 2.37 times more likely to have OLP compared to those whose thyroids were working well.
This finding adds to the growing understanding of how hypothyroidism can impact different aspects of health.
There are two reasons why an underactive thyroid might bring about a condition like OLP.
The most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, which is an autoimmune disease. In autoimmune diseases, your body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues.
When your immune system mistakenly attacks your thyroid gland, it might be generally too active, attacking other tissue around your body as well with an inflammatory response. This can directly cause OLP.
Even if hypothyroidism isn’t caused by an autoimmune disease, low thyroid hormone levels can upset the balance in the cellular processes involved in inflammation.

 Overcoming IBD
Overcoming IBD Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple Sclerosis Banishing Bronchitis
Banishing Bronchitis Gum Disease Gone
Gum Disease Gone Overcoming Onychomycosis
Overcoming Onychomycosis Neuropathy No More
Neuropathy No More The Prostate Protocol
The Prostate Protocol Brain Booster
Brain Booster
 Ironbound
Ironbound
 Solution for Shingles
Solution for Shingles
 The Bone Density Solution
The Bone Density Solution
 The Ultimate Healing Protocol
The Ultimate Healing Protocol
 The Parkinson's Protocol
The Parkinson's Protocol
 The Chronic Kidney Disease Solution
The Chronic Kidney Disease Solution
 Overthrowing Anxiety
Overthrowing Anxiety The Fatty Liver Solution
The Fatty Liver Solution The Hypothyroidism Solution
The Hypothyroidism Solution
 The End of Gout
The End of Gout The Blood Pressure Program
The Blood Pressure Program
 The Oxigized Cholesterol Strategy
The Oxigized Cholesterol Strategy
 Stop Snoring And Sleep Apnea Program
Stop Snoring And Sleep Apnea Program
 The Arthritis Strategy
The Arthritis Strategy The Vertigo & Dizziness Program
The Vertigo & Dizziness Program The 3-Step Diabetes Strategy
The 3-Step Diabetes Strategy Hemorrhoids Healing Protocol
Hemorrhoids Healing Protocol The Erectile Dysfunction Master
The Erectile Dysfunction Master Weight Loss Breeze
Weight Loss Breeze The IBS Program
The IBS Program The Insomnia Program
The Insomnia Program The Migraine and Headache Program
The Migraine and Headache Program The Neck Pain Solution
The Neck Pain Solution The Menopause Solution
The Menopause Solution The Ejaculation Master
The Ejaculation Master The TMJ Solution
The TMJ Solution The Acid Reflux Solution
The Acid Reflux Solution The Fibromyalgia Solution
The Fibromyalgia Solution The Psoriasis Strategy
The Psoriasis Strategy