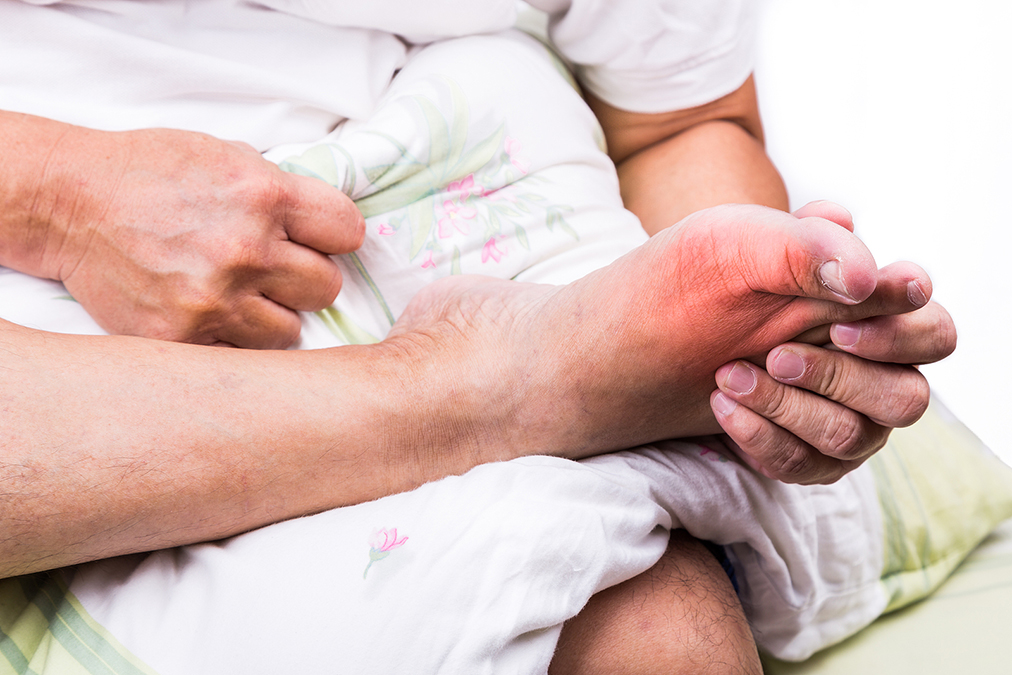
 Gout is caused by the accumulation of urate crystals in our joints when there’s too much uric acid in our blood, a condition known as hyperuricemia.
Gout is caused by the accumulation of urate crystals in our joints when there’s too much uric acid in our blood, a condition known as hyperuricemia.
The first thing you were probably told to do when diagnosed with gout was to cut down on meat, especially red meat because that’s very high in uric acid.
Here’s the dilemma: if meat was really the cause of gout, then vegetarians would never develop gout, right?
A new study in the Journal of the Chinese Medical Association put this common-sense question to a test and the results were surprising.
Conducted between 2005 and 2016, this study aimed to create prediction models for hyperuricemia among vegetarians.
The scientists recruited a big sample of 7,331 adult vegetarians, 593 with hyperuricemia and 6,738 with normal uric acid levels. This proves clearly that, while a vegetarian diet is generally beneficial, it doesn’t entirely eliminate the risk, with around 92% of vegetarians still being at risk of gout.
Digging deeper into the risk factors, the study uncovered the following as potential risk factors for hyperuricemia in vegetarians.
-
1. Male gender.
2. High levels of fats in the blood.
3. High body mass index score.
4. High albumin in the blood, which is a category of protein that regulates blood pressure and transports nutrients around our bodies.
On the flip side, a higher estimated glomerular filtration rate, which indicates better kidney function, was linked with a lower risk of hyperuricemia in vegetarians.
The implication of this finding is that, while adopting a vegetarian diet is a step in the right direction for managing gout and hyperuricemia, it’s not a foolproof strategy.
This should perhaps not be surprising, as vegetarian diets can be very unhealthy if sugary treats, refined carbohydrates, hydrogenated fats, and salty canned and packaged foods are included in them.
Another reason why a vegetarian diet isn’t foolproof is that only a small percent of gout cases is caused by consuming too much uric acid. The real underlying mechanism of gout is your body’s inability to remove uric acid from your body.

 Overcoming IBD
Overcoming IBD Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple Sclerosis Banishing Bronchitis
Banishing Bronchitis Gum Disease Gone
Gum Disease Gone Overcoming Onychomycosis
Overcoming Onychomycosis Neuropathy No More
Neuropathy No More The Prostate Protocol
The Prostate Protocol Brain Booster
Brain Booster
 Ironbound
Ironbound
 Solution for Shingles
Solution for Shingles
 The Bone Density Solution
The Bone Density Solution
 The Ultimate Healing Protocol
The Ultimate Healing Protocol
 The Parkinson's Protocol
The Parkinson's Protocol
 The Chronic Kidney Disease Solution
The Chronic Kidney Disease Solution
 Overthrowing Anxiety
Overthrowing Anxiety The Fatty Liver Solution
The Fatty Liver Solution The Hypothyroidism Solution
The Hypothyroidism Solution
 The End of Gout
The End of Gout The Blood Pressure Program
The Blood Pressure Program
 The Oxigized Cholesterol Strategy
The Oxigized Cholesterol Strategy
 Stop Snoring And Sleep Apnea Program
Stop Snoring And Sleep Apnea Program
 The Arthritis Strategy
The Arthritis Strategy The Vertigo & Dizziness Program
The Vertigo & Dizziness Program The 3-Step Diabetes Strategy
The 3-Step Diabetes Strategy Hemorrhoids Healing Protocol
Hemorrhoids Healing Protocol The Erectile Dysfunction Master
The Erectile Dysfunction Master Weight Loss Breeze
Weight Loss Breeze The IBS Program
The IBS Program The Insomnia Program
The Insomnia Program The Migraine and Headache Program
The Migraine and Headache Program The Neck Pain Solution
The Neck Pain Solution The Menopause Solution
The Menopause Solution The Ejaculation Master
The Ejaculation Master The TMJ Solution
The TMJ Solution The Acid Reflux Solution
The Acid Reflux Solution The Fibromyalgia Solution
The Fibromyalgia Solution The Psoriasis Strategy
The Psoriasis Strategy