 This is the most important ingredient for our brain. Without it, you’d die within minutes.
This is the most important ingredient for our brain. Without it, you’d die within minutes.
But according to a new study in the journal Biomedicines, something can go terribly wrong with this ingredient.
And when that happens, it attacks your brain—causing Alzheimer’s and other forms of dementia.
For those who have heard of oxidative damage but aren’t sure what it really means, here is a crash course.
When an apple is exposed to oxygen, it turns brown. This is because, in chemical terms, the interaction between the apple and the oxygen begins a process called oxidation, in which the oxygen robs the apple of electrons. The apple is suffering oxidative damage because it is transferring its essential electrons to the oxygen.
If this process goes on for too long, the apple will disintegrate completely and turn into something like a powder.
Oxygen is a major oxidizing agent, not only of apples, but also of cells inside your body. Your brain uses more oxygen than your other organs, so with all this oxygen in your brain, it is inevitable that some cell damage will take place.
In this new study, scientists used mice that were genetically modified to ensure that they would develop Alzheimer’s disease. They also used mice without Alzheimer’s as a comparison.
They used six groups of mice: three-month-old, six-month-old, and 20-month-old mice with Alzheimer’s disease, along with healthy mice at each of these three age groups.
They put these mice through two tests: the Morris water maze and the Rota-rod test.
Both of these tests confirmed that the Alzheimer’s mice were cognitively impaired, but that their motor and coordination abilities were normal.
To find out whether oxidative damage was involved in this cognitive impairment, they collected tissue samples from the mouse brains and measured the markers of such damage.
-
1. They found high levels of 3-nitrotyrosine, a marker of oxidation, in the brains of the Alzheimer’s mice.
2. They found very low levels of NMNAT-3, a chemical that has antioxidant effects, in the brains of the Alzheimer’s mice.
Therefore, they concluded that the progression of Alzheimer’s was caused by oxidative damage.
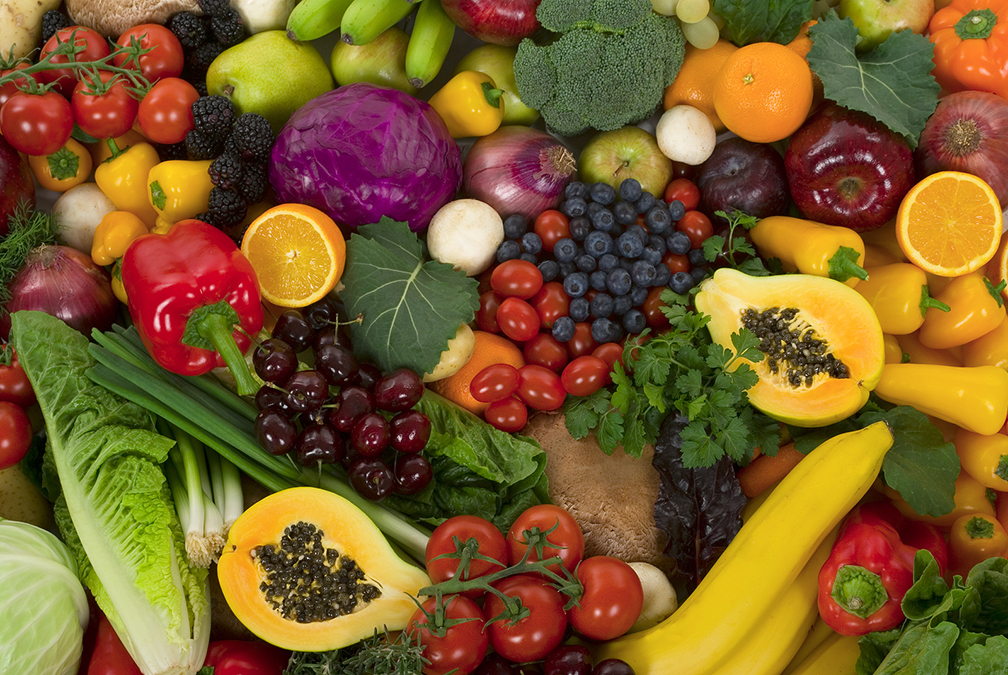
This is why you should incorporate as many antioxidants as possible into your diet. An antioxidant is a substance that has plenty of electrons to donate to your brain cells that have had theirs stolen by oxygen. Here are some powerful antioxidants and good sources for each of them:
-
1. Vitamin C: Kale, Swiss chard, spinach, broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage, asparagus, sweet and bell peppers, tomatoes, guava, kiwifruit, oranges, strawberry, raspberry, blackberry, blueberry, pineapple, mango, and papaya.
2. Vitamin E: Spinach, Swiss chard, broccoli, squash, pumpkin, sweet potato, avocado, olive oil, coconut oil, almonds and most nuts, sunflower seeds and most other seeds, crayfish, trout, and salmon.
3. Vitamin A: Yellow and orange starchy vegetables, the same greens listed above, tuna, oysters, milk, peppers, paprika, basil, tomato, and mango.
4. Flavonoids: Rosemary, cucumber, broccoli, cauliflower, sweet potato, cocoa, berries, red wine, dark grapes, capers, apple, and curry.
In other words, eat plenty of fruits and vegetables for a high-antioxidant diet.

 Overcoming IBD
Overcoming IBD Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple Sclerosis Banishing Bronchitis
Banishing Bronchitis Gum Disease Gone
Gum Disease Gone Overcoming Onychomycosis
Overcoming Onychomycosis Neuropathy No More
Neuropathy No More The Prostate Protocol
The Prostate Protocol Brain Booster
Brain Booster
 Ironbound
Ironbound
 Solution for Shingles
Solution for Shingles
 The Bone Density Solution
The Bone Density Solution
 The Ultimate Healing Protocol
The Ultimate Healing Protocol
 The Parkinson's Protocol
The Parkinson's Protocol
 The Chronic Kidney Disease Solution
The Chronic Kidney Disease Solution
 Overthrowing Anxiety
Overthrowing Anxiety The Fatty Liver Solution
The Fatty Liver Solution The Hypothyroidism Solution
The Hypothyroidism Solution
 The End of Gout
The End of Gout The Blood Pressure Program
The Blood Pressure Program
 The Oxigized Cholesterol Strategy
The Oxigized Cholesterol Strategy
 Stop Snoring And Sleep Apnea Program
Stop Snoring And Sleep Apnea Program
 The Arthritis Strategy
The Arthritis Strategy The Vertigo & Dizziness Program
The Vertigo & Dizziness Program The 3-Step Diabetes Strategy
The 3-Step Diabetes Strategy Hemorrhoids Healing Protocol
Hemorrhoids Healing Protocol The Erectile Dysfunction Master
The Erectile Dysfunction Master Weight Loss Breeze
Weight Loss Breeze The IBS Program
The IBS Program The Insomnia Program
The Insomnia Program The Migraine and Headache Program
The Migraine and Headache Program The Neck Pain Solution
The Neck Pain Solution The Menopause Solution
The Menopause Solution The Ejaculation Master
The Ejaculation Master The TMJ Solution
The TMJ Solution The Acid Reflux Solution
The Acid Reflux Solution The Fibromyalgia Solution
The Fibromyalgia Solution The Psoriasis Strategy
The Psoriasis Strategy