 An arthritis diagnosis sounds like a sentence to a life, accompanied by pain, disability, and expensive medication and their side effects.
An arthritis diagnosis sounds like a sentence to a life, accompanied by pain, disability, and expensive medication and their side effects.
A new study by researchers from the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine published in the journal Frontiers – Nutrition concludes that it doesn’t have to be this way.
The team performed a review of existing studies and found that a surprising (and controversial) diet could reverse arthritis without drugs.
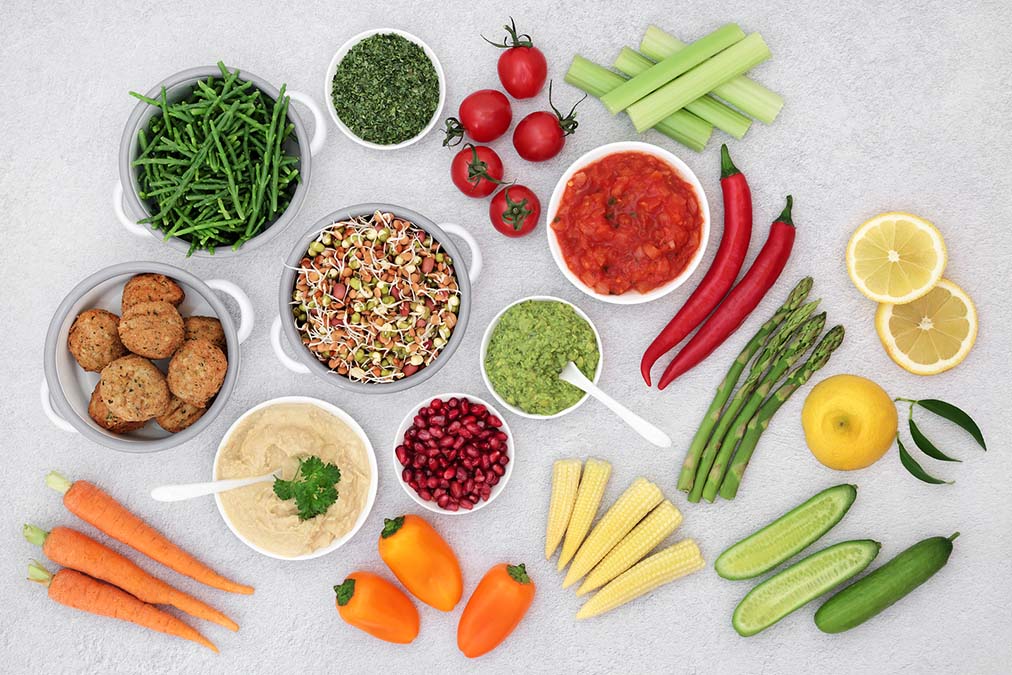
Firstly, they found that plant-based diets were great at reducing inflammation, which is at the heart of arthritis.
From the majority of existing studies, they concluded that diets that contained a lot of meat and dairy were the most likely to cause inflammation.
C-reactive protein, one of the chief contributors to inflammation, was found to be much higher in people who consumed meat and dairy than in people who did not.
Secondly, with the exception of fish, olive oil, and avocado, excessive fat consumption worsens inflammation and arthritis symptoms. A lot of the fats in the typical Western diet come from meat, dairy, and eggs, proving why plant-based diets help.
Of course, this is not always true. If you turn vegan but load your diet with vegetable oils, your arthritis symptoms will remain.
Thirdly, people who consume plant-based diets lose more weight and maintain a healthier weight than those who eat animal-based foods. This reduces the weight they load on their joints, which prevents them from deteriorating as fast as those of overweight people.
But it is not necessarily true in all cases. A vegan diet filled with white bread and other refined grains will not result in weight loss.
Also, because of all the vegetables and whole grains, plant-based diets contain more fiber and other nutrients compared to the typical Western animal-based diet. This is great for cultivating a great variety of gut bacteria which, while sounding gross, is precisely what you want.
Finally, the studies revealed people who ate mostly plants suffered from a lot less pain than people who consumed animal-based products, which could have been due to the reduction in inflammation.

 Overcoming IBD
Overcoming IBD Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple Sclerosis Banishing Bronchitis
Banishing Bronchitis Gum Disease Gone
Gum Disease Gone Overcoming Onychomycosis
Overcoming Onychomycosis Neuropathy No More
Neuropathy No More The Prostate Protocol
The Prostate Protocol Brain Booster
Brain Booster
 Ironbound
Ironbound
 Solution for Shingles
Solution for Shingles
 The Bone Density Solution
The Bone Density Solution
 The Ultimate Healing Protocol
The Ultimate Healing Protocol
 The Parkinson's Protocol
The Parkinson's Protocol
 The Chronic Kidney Disease Solution
The Chronic Kidney Disease Solution
 Overthrowing Anxiety
Overthrowing Anxiety The Fatty Liver Solution
The Fatty Liver Solution The Hypothyroidism Solution
The Hypothyroidism Solution
 The End of Gout
The End of Gout The Blood Pressure Program
The Blood Pressure Program
 The Oxigized Cholesterol Strategy
The Oxigized Cholesterol Strategy
 Stop Snoring And Sleep Apnea Program
Stop Snoring And Sleep Apnea Program
 The Arthritis Strategy
The Arthritis Strategy The Vertigo & Dizziness Program
The Vertigo & Dizziness Program The 3-Step Diabetes Strategy
The 3-Step Diabetes Strategy Hemorrhoids Healing Protocol
Hemorrhoids Healing Protocol The Erectile Dysfunction Master
The Erectile Dysfunction Master Weight Loss Breeze
Weight Loss Breeze The IBS Program
The IBS Program The Insomnia Program
The Insomnia Program The Migraine and Headache Program
The Migraine and Headache Program The Neck Pain Solution
The Neck Pain Solution The Menopause Solution
The Menopause Solution The Ejaculation Master
The Ejaculation Master The TMJ Solution
The TMJ Solution The Acid Reflux Solution
The Acid Reflux Solution The Fibromyalgia Solution
The Fibromyalgia Solution The Psoriasis Strategy
The Psoriasis Strategy