 University of Queensland researchers revealed in the latest edition of the journal Science Translational Medicine, that they have found a non-invasive nonpharmacological strategy to cure Alzheimer’s disease.
University of Queensland researchers revealed in the latest edition of the journal Science Translational Medicine, that they have found a non-invasive nonpharmacological strategy to cure Alzheimer’s disease.
It’s effective, safe and cheap. Requires no drugs and most physical therapists and doctors already have the technology in place to perform this task.
To understand the contribution they have made, we must take a detour through the physical manifestation of Alzheimer’s.
It begins when there is an excess of a peptide called amyloid-beta inside your brain. Huge amounts of this peptide congregate inside and between your brain cells, forming a dense layer or plaque throughout your brain.
This plaque then interferes with the ability of your cells to communicate with each other, and ultimately destroys your brain cells completely.
At this stage scientists still disagree about why these plaques form, but it is obvious that your body produces too much amyloid-beta and/or your brain’s ability to remove it becomes impaired.
Scientists have, as a result, tried to invent drugs that either prevent your body from producing this peptide, or that boost your brain’s ability to remove excess amounts of it.
But, as the Australian researchers recall from previous studies, these drugs have rather extreme side effects and have not been terribly effective anyway.
They have now tested a new therapy on mice with considerable success.
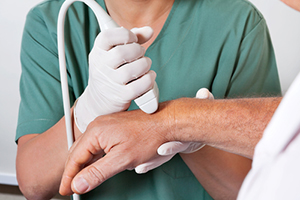
They used a focused therapeutic ultrasound (similar to what physical therapists use for muscle stimulation). This device broadcasts sound waves into your brain tissue.
These sound waves vibrate very fast, and are thereby able to cause two processes that might be responsible for Alzheimer’s relief.
1) First, they open your blood/brain barrier very slightly and gently, which the researchers speculated may prevent newly produced amyloid-beta from being deposited inside your brain.
2) Second, and more importantly, it can clear amyloid-beta plaques that have already formed.
It does so by activating your microglia, which are cells inside your brain responsible for clearing away waste. Once your microglia are activated by the ultrasound, they can remove the plaques.
When they subjected mice to tests, they found that this treatment had restored the memory function of 75 percent of the mice on which they used it.
Their function improved in learning to navigate a maze, in learning to recognize new objects, and in memorizing places they needed to avoid.
Best of all, the scientists found absolutely no brain damage after applying the ultrasound treatment.
They now want to test their therapy on larger mammals, after which they want to obtain permission to start human trials.
This is a huge discovery and, if it turns out that it works on humans, it will be a cheap, safe and effective way to combat this disease from which approximately 50 million people worldwide suffer.

 Overcoming IBD
Overcoming IBD Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple Sclerosis Banishing Bronchitis
Banishing Bronchitis Gum Disease Gone
Gum Disease Gone Overcoming Onychomycosis
Overcoming Onychomycosis Neuropathy No More
Neuropathy No More The Prostate Protocol
The Prostate Protocol Brain Booster
Brain Booster
 Ironbound
Ironbound
 Solution for Shingles
Solution for Shingles
 The Bone Density Solution
The Bone Density Solution
 The Ultimate Healing Protocol
The Ultimate Healing Protocol
 The Parkinson's Protocol
The Parkinson's Protocol
 The Chronic Kidney Disease Solution
The Chronic Kidney Disease Solution
 Overthrowing Anxiety
Overthrowing Anxiety The Fatty Liver Solution
The Fatty Liver Solution The Hypothyroidism Solution
The Hypothyroidism Solution
 The End of Gout
The End of Gout The Blood Pressure Program
The Blood Pressure Program
 The Oxigized Cholesterol Strategy
The Oxigized Cholesterol Strategy
 Stop Snoring And Sleep Apnea Program
Stop Snoring And Sleep Apnea Program
 The Arthritis Strategy
The Arthritis Strategy The Vertigo & Dizziness Program
The Vertigo & Dizziness Program The 3-Step Diabetes Strategy
The 3-Step Diabetes Strategy Hemorrhoids Healing Protocol
Hemorrhoids Healing Protocol The Erectile Dysfunction Master
The Erectile Dysfunction Master Weight Loss Breeze
Weight Loss Breeze The IBS Program
The IBS Program The Insomnia Program
The Insomnia Program The Migraine and Headache Program
The Migraine and Headache Program The Neck Pain Solution
The Neck Pain Solution The Menopause Solution
The Menopause Solution The Ejaculation Master
The Ejaculation Master The TMJ Solution
The TMJ Solution The Acid Reflux Solution
The Acid Reflux Solution The Fibromyalgia Solution
The Fibromyalgia Solution The Psoriasis Strategy
The Psoriasis Strategy